Welders are professionals well-versed with the different welding processes. A welder uses numerous welding techniques to fabricate metal joints and components found in various industries and industrial products.
Welders are also responsible for ensuring that welding practices adhere to the prescribed quality and safety standards. They prepare materials and equipment for welding, inspecting, and analyzing the welded products to identify welding defects and their sources.
Table of Contents
What Is Welding? What Is the Role of a Welder?
-
Apply for a welding degree at NEIT!
Loading…
/**/
Welding is the process of joining metals by applying heat, pressure, or a combination of both.
When two metal parts are to be connected, heat and pressure help melt the two metals. Once the molten metal solidifies, the two parts connect together with a permanent bond.
You can create leak-proof joints, avoid vibrations due to loose fasteners, and even perform underwater welding. Since welding is a low-cost process and provides high joint strength, it remains one of the most preferred choices for joining metals.
Can you think of a sector where you don’t require the joining of metals? Metal joints find their use in bridges, structures, housing, automobiles, trains, power plants, oil refineries, and many such areas. Wherever there’s metal to be joined, there’s welding to be had!
What Are the Different Types of Welding?
Depending upon the metals you want to join, the strength of joints desired, and ease of operation, you can use one of the several weldings.
If you are looking to become a welder, you can gain expertise in any of the following techniques. The most commonly used methods of welding are:
Arc Welding
Arc welding uses an electric arc from an external power supply source to generate heat to melt and join metals. The power supply connects to the electrode that carries current or melts directly into the weld pool due to the applied heat.
This welding method is simple, inexpensive, fast, and reliable. You can find the applications of arc welding in the automotive, shipbuilding, and construction industries.
Flux-Coated Arc Welding (FCAW)
FCAW is a variation of arc welding. The electrode used for FCAW contains a flux that protects the weld pool from contamination. FCAW has a high metal deposition rate, making it ideal for high-speed applications like mass production lines.
Mild steel, low-alloy steel, and stainless steel are common materials that you can join using FCAW.
Shielded-Metal Arc Welding(SMAW)
SMAW is very similar to flux-coated arc welding. The only difference between SMAW and FCAW is that SMAW electrodes are solid and have an external covering of flux, while FCAW electrodes have a tubular shape with an inner flux core.
Gas Metal Arc Welding(GMAW)
Gas-metal Arc Welding(GMAW) or metal inert gas welding(MIG) uses a consumable wire-type electrode. A shielding inert gas flows through the welding gun and helps protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Originally developed for aluminum and other non-ferrous metals, GMAW is now used for welding steel and its alloys.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding(GTAW)
GTAW or tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding is highly popular as it uses a non-consumable electrode. A tungsten electrode and a filler metal help create a joint between the two metals.
Inert gases such as argon or helium protect the area being welded from contamination, and most, although not all, welding applications will require filler metal.
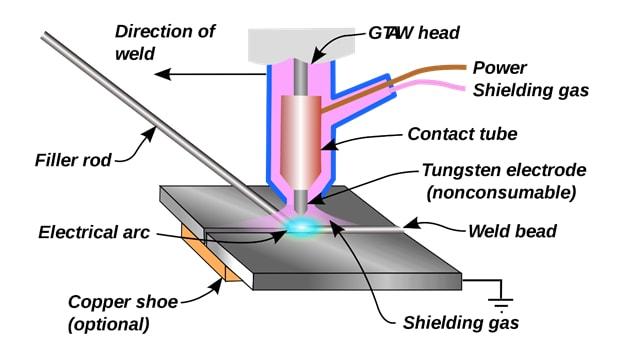
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_tungsten_arc_welding#/media/File:GTAW.svg
START YOUR WELDING CAREER
Earn your degree in Welding Engineering Technology from NEIT and begin your new career path today!
ASSOCIATE'S DEGREE
BACHELOR'S DEGREE
Job Responsibilities of A Welder
Let’s take a look at the job responsibilities and the job description of a welder. Welders work in the manufacturing and construction industry and similar areas depending upon their skills and experience level.
A welder’s job description may involve one of the following responsibilities:
- Fabrication of metal joints and products
- Studying and analyzing drawings, blueprints, and sketches about metal joints.
- Calculating the dimension of weld required for securing the metal parts to be connected
- Ensuring that the workpiece adheres to prescribed quality and safety standards
- Performing on-site inspections to check for defects and deviations
- Recommending welding methods for joining a particular set of metals
- Executing post-welding operations such as filling of holes, deburring, and hammering out the bulges and bends
- Maintenance of the welding equipment and machinery
What are the Requirements for Becoming A Welder?
Given the scope, there is always a high demand for skilled people in the welding industry. If you want to take up a welding job or become a certified welding inspector, these are some of the requirements you must fulfill:
Education
If you wish to become a welder, you will need a GED or high school diploma. Once you’ve obtained your GED, you can apply for a welding certificate program.
A typical welding certification program can take six to eighteen months. During your certification program, you will learn the various welding methods and techniques. To further enhance your employability, you can pursue an apprenticeship program for additional and on-the-job-training.
An Associate Degree in Welding Engineering Technology can pave the path for a fulfilling career. Students will learn the theory and undergo welding training for joining materials using the various welding processes during this two-year welding program.
Your college might also engage you with construction projects or manufacturing jobs during your apprenticeship to enhance your skills as a welder.
Training
Along with the prerequisite education, training is an important part of becoming a welder. During their training and certification programs, welders work on live projects full time at the actual job location and handle welding equipment to complete their welding duties.
While working, the job instructor or shop floor manager will also teach welders about the various safety protocols important for handling power tools and equipment.

Certifications
To fulfill your job duties as a welder, you can also take up one of the certification programs. Some of the most popular types of welding certificates are as follows:
- Certified Welder (CW)
- Certified Welding Inspector (CWI)
- Senior Certified Welding Inspector (SCWI)
- Certified Welding Educator (CWE)
- Certified Welding Sales Representative (CWSR)
- Certified Associate Welding Inspector (CAWI)
- Certified Radiographic Interpreter (CRI)
- Certified Robotic Arc Welding (CRAW)
- Certified Welding Supervisor (CWS)
- Certified Welding Engineer (CWE)
Skills
As a welder, you must also possess these traits for welding mechanical structures, construction products, and surfaces and performing a variety of welding jobs:
- Physical fitness
- Great attention to detail
- Good dexterity and vision
- Good communication skills
- Ability to solve real-life problems
- Troubleshooting abilities
- Knowledge of welding specifications
What Industries Do Welders Work In?
Some of the top industries that offer attractive job offers to welders are:
- Mechanical, Architectural, and Structural Products Industry
- Mining, Agriculture & Construction Machinery
- Motor Vehicle, Heavy Automotive, Trailers, and Bodies fabrication
- General-Use Machinery

Other Employers of Welders
In addition to the above sectors, welders may also work as:
- Specialty Trade Contractors
- Self-Employed Welders
- Repair & Maintenance Specialists
- Wholesalers of Durable Goods
- Construction Welders
What Is the Workplace Environment Of a Welder Like?
There is a common misconception that welders work in hazardous conditions. However, the use of safety gear and equipment has helped create a safe workplace for industry workers.
A regular 40-hour working scheduling is common among welders. You can also improve your earnings by working overtime as there is a huge demand for welding.
Workers in the manufacturing and construction industry or repair work may join metal parts located at a great height and be at risk of accidents. Such factors make it essential for a welder to adhere to the guidelines taught during their job training or degree.
How Much Does a Welder Earn?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), welders earned median annual pay of $42,490 or $20.43 per hour in 2019. In the same year, the top ten percent of welders earned as much as $64,240. Since working overtime is common among welders, a large number of welders work a 12-hour shift daily. It is projected that in the next ten years, welders’ employment will increase by 3%.
How to Become a Welder?
The process of becoming a welder can be roughly divided into four steps. They are:
- Earn a High School Diploma or GED: A high-school diploma helps provide the basic foundation necessary for taking up any job. As welders require technical expertise, the arithmetic, and geometry that you learn initially help a lot.
- Get a Certification or a Degree in Welding: You can obtain your certification or associate’s degree from the USA’s best colleges for welding to improve your prospects of a fulfilling career. Certification programs usually last from six to eighteen months, while an associate degree generally takes two years.
- Participate in Training or Apprenticeship: As a welder taking up apprenticeships in a manufacturing, structural, or repair company can help learn the trade practically. With the hands-on welding experience in joining various metal surfaces and metal parts, your skills improve, and your career can get off to a good start.
- Earn a Welding Certification: Getting certified is a great way to validate your knowledge of welding and also highlight your level of expertise to potential employers. The American Welding Society (AWS) issues most of these certificates.
Ready to kickstart your welding career? Visit our website to learn more about our full-time courses and degree programs in welding technology.
START YOUR WELDING CAREER
Earn your degree in Welding Engineering Technology from NEIT and begin your new career path today!
ASSOCIATE'S DEGREE
BACHELOR'S DEGREE
FAQs
Where do welders usually work?
Welders work in the manufacturing, structural engineering, and fabrication industry for joining metals and components.
What things do welders make?
Welders fabricate metal joints essential for creating an assembly or repair and maintenance of products.
Do welders make good money?
The median pay of welders was $42490 per year in 2019. There is also scope to earn more by working overtime.
Is a welder a good job?
Being a welder is a good job as you can get decent pay and earning opportunities. Working in essential sectors also gives good job satisfaction, making welding a great career option.

