With a mean annual wage of $56,900, an increasing number of people are looking into life as an electrician. Unsurprisingly, enrolling in an electrician trade school is one of the most popular ways to break into the field.
Though the certification process is rigorous, the rewards of working as a certified electrician is well worth the effort. Training programs vary widely across the country based on duration, content, and accreditation.
This article will walk you through different ways to become an electrician, skills, license requirements, salary outlook, electrician trade school, and apprenticeship options. Our goal is to help students and professionals make informed decisions about their future career.
Table of Contents
What Do Electricians Do?
Many electricians start their careers as apprentices with a licensed contractor or a company specializing in electrical contracting. After completing an apprenticeship, the majority of electricians move on to become a licensed journeyman or master electrician.
So, what do electricians do, exactly? Well, they install, maintain, and troubleshoot electrical power, lighting, and communication and control systems. An electrician’s skills can be applied to both residences and commercial establishments.
START YOUR ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY CAREER
Earn your degree in Electrical Technology from NEIT and begin your new career path today!
ASSOCIATE'S DEGREE
BACHELOR'S DEGREE
The Two Pathways to Becoming an Electrician

Aspiring electricians can either join a trade school followed by an apprenticeship training program or enter an apprenticeship program directly. However, those who go through a trade school have access to better jobs, higher salary potential, career stability, and the ability to make good industry connections.
Let’s take a closer look into both options and what they entail.
Trade Schools
An electrician trade school gives you 8 to 12 months of practical training while you study. Most programs cover electrical, HVAC, solar, and wind energy concepts. The focus of a trade school is to get you on the field and into a job fast.
Learning in a trade school gives you room to make mistakes and practice the necessary skills. You can also get tutoring if you need extra help understanding certain subjects. If you directly apply for an apprenticeship, you need to be prepared to work under the watchful eye of your employer. This reduces the margin for errors allowed on the job.
Getting into a Trade School
You’ll need a high school diploma to enroll in an electrical trade school (or equivalent). There may be entrance exams and a general aptitude test depending on the program.
The Cost of Becoming an Electrician
The costs of becoming an electrician vary greatly depending on the program type and location. According to the U.S. Department of Education, the average cost of tuition and fees is $14,632.
Some programs cost as little as $299 or a few thousand dollars. Others are priced at $40,000 or higher. Contact the admissions office at your target school to learn more about tuition and fees.
Electrician Training Programs and Degrees
There are many electrician training programs and degrees available to those who want to become electricians. Some programs may require just a few months of training, while others may take several years.
Certificate Program
These programs take a year or less to complete. Students will learn about wiring, national electrical code, electrical safety, power distribution, and industrial control. You should only select an electrician certification program if you intend to enroll in an apprenticeship immediately after completing the course.
Associate Degree
These programs take around two-years to complete. Students will learn about accidental prevention, electrical theory, electrical inspection, lighting, transformers, electrical contracting, and project management. They will also receive pre-apprenticeship training during this window.
Bachelor’s Degree
These programs involve a mix of practical electrician skills and theory. The skills and courses include regulation and policy, digital electronics, mathematics, electrical trends, electrical theory, linear and integrated circuits, and solid-state devices.
The Best Electrician Schools and Programs in Rhode Island
Electrician training programs and degrees vary by state, but the core curriculum is generally the same. Rhode Island has two schools that offer electrician programs:
New England Institute of Technology
The New England Institute of Technology offers an associate degree in electrical technology, providing the necessary hours to become a licensed electrician. Graduates of the electrician schools can apply for entry-level electrical work or apprenticeship programs.
Community College of Rhode Island
The Community College of Rhode Island provides an apprenticeship training program for individuals aspiring to become a licensed journeyman electrician. This is a four-year electrician training program where students have to work in an apprenticeship during the day and take evening classroom instruction.
There are several electrician trade schools and programs across the U.S.
Apprenticeships
An electrician apprenticeship program provides on-the-job instruction and practice. Before you begin, it’s important to be comfortable with hand and power tools, climbing ladders without the fear of height, working in tight spaces, and under different weather conditions.
Here are the basic steps to getting into an apprenticeship program:
- Groundwork – Research about the jobs and talk to other professionals. Understand how the profession works and study the electrical code. Browse the job postings and understand what is available in the market.
- Get a high school diploma – You will likely need a high school diploma or GED to become an electrician apprentice. One year of algebra with additional math and science courses will help you understand the principles of electricity and circuitry.
- Get into an electrician training program – Before joining an apprenticeship, you need to show your skills and competency. Choose a program that teaches you the fundamentals, electrical code, and safety. You will need hands-on work and classroom sessions to understand actual electrical units, industry equipment, and distribution systems.
- Find an apprenticeship sponsor – An apprenticeship is a fundamental step to becoming a journeyman electrician or a master electrician. Research the company offering the apprenticeship, get your resume up-to-date, and communicate how you can help the company throughout the program.
Types of Apprenticeships for Electricians
Depending on your area of interest, you may choose any of the following apprenticeships:
1. Residential apprentice – You will be responsible for installing residential wiring, switches, plugs, CAT-5 and RG-6 cables, and electrical panels. Apprentices may also troubleshoot electrical problems in homes and apartments.
Typical duties of a residential apprentice include:
- Installing fire alarms
- Establishing grounding systems
- Setting up temporary power during construction
- Installing new wiring and repairing old wiring
- Installing lighting systems, receptacles, and fixtures
- Troubleshooting electrical systems
It is fast-paced work, and electricians may have to complete a job within two to three days. This is a great niche if you want to learn home automation upgrades and eventually start a business.
2.Inside wireman apprentice – Inside wireman or commercial electrician works in non-residential projects. Commercial buildings include gas stations, schools, offices, industries, and non-residential structures.
New constructions need a lot of manpower, which is a hot spot for new talent. Typical duties of an inside wireman are:
- Initiation and planning of the projects
- Establishing temporary power
- Setting up grounding systems
- Establishing power distribution
- Planning and installing raceway systems
- Setup motors, HVAC systems, and other equipment
- Installing and repairing outdoor lighting, traffic signals, and outdoor power feeders
- Installing fire alarms
As an inside wireman apprentice, you will enjoy the opportunity to learn quickly, accelerating your path to becoming a licensed electrician.
Application Requirements
To become an apprentice, you must possess basic knowledge of electric work. It would help if you showed initiative rather than waiting for instruction. On the technical front, you will need basic tools and protective clothing.
If an organization pays for an apprenticeship, they’ll have rules to ensure that an apprentice will not leave mid-way.
How to Find an Apprenticeship Program
You can find apprenticeship jobs in the following ways:
- Local job boards – Whether it is a local newspaper or an advertisement in the supermarket, it is always a good idea to start in your neighborhood. It will be easier to do the due diligence.
- U.S. Department of Labor – The registered apprenticeship program offers avenues for employers and employees to connect.
- Independent contractors – The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides an apprenticeship scheme for budding electrician apprentices.
- National Electrical Contractors’ Association & International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers – The NECA & IBEW are partners with national and national joint apprenticeship training committees and centers (JATC).
Electrician Trade School Vs. Apprenticeship – Which is Better?

Let’s take a look at the differences between a trade school electrician program and an apprenticeship program:
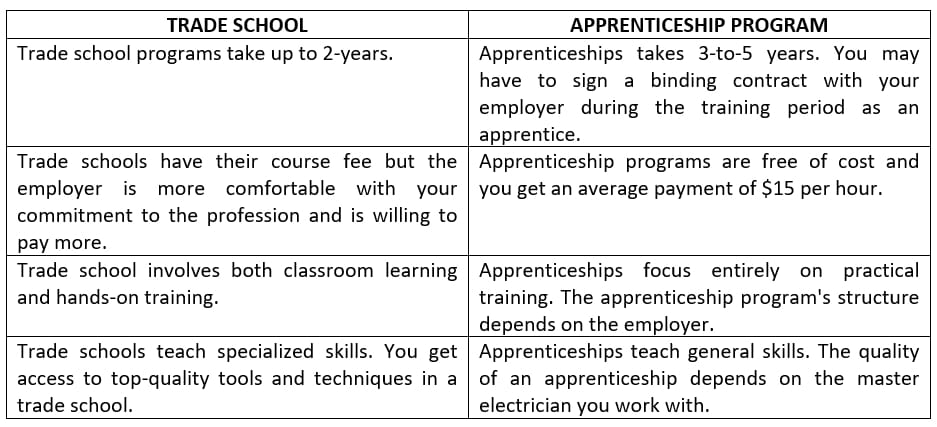
Both trade school electrician programs and apprenticeship programs provide you with ample opportunities to make industry connections. The kind of opportunities you enjoy depends on your technical and interpersonal skills.
An Electrician’s Career: What You Need to Know
An electrician program provides numerous job opportunities for a satisfying career. With over 66,000 annual job openings and 9% projected growth between 2020 and 2030, an electrician’s employment continues to be in high demand.
Electrician Job Categories and Specializations
You can categorize electrician jobs into five main groups: design, installation, maintenance, repair, and modification. In addition to these five main categories, there are also several specialized jobs, such as:
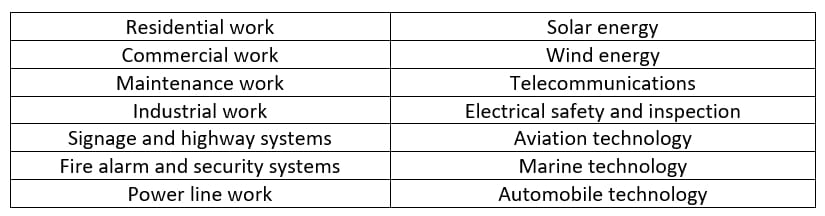
The specific duties will vary depending on the job category that they are working in.
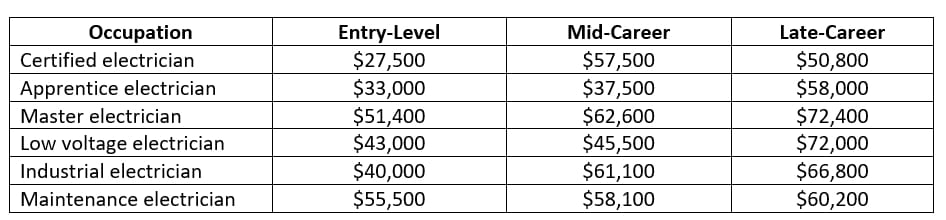
Salary Outlook
The table below shows the annual median salary of electricians:
License Requirements
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is the acceptable code for licensing. The laws for low-voltage work vary from state to state.
The Department of Labor and Training, Rhode Island, defines the state’s license requirements and all laws, rules, and regulations.
What States Do Not Require an Electrician License?
There are a few exceptions. The states of Iowa, Kansas, Mississippi, New Hampshire, North Dakota, Ohio, and Wisconsin do not have any low-voltage licensing requirements. Colorado, Indiana, Missouri, and Pennsylvania do not have any state-wide requirements but may have location-wise licensing requirements.
What Skills Do Electricians Need?

The top skills required to be a successful electrician are:
- Problem-solving – Diagnosing a problem and devising corrective solutions require problem-solving capability. Electricians must think out of the box to solve problems on-site. They need to familiarize themselves quickly with the electrical system at home or place of business.
- Open to learning – Electricians must have a keen interest in mathematics and physics and develop practical skills. Learning new skills and staying updated with the latest technologies can improve the quality of an electrician’s work.
- Customer service – Electricians interact with the client, especially those for in-home repairs. They need to have good communication and listening skills when interacting with the client. The technicians may need to do follow-up calls after completing the service.
- Time management – Electricians visit more than one site a day and need to adhere to strict timelines. They need to estimate correctly the time required and avoid arriving late to a job site. Delays cause inflated project costs and reputation damage.
- Ability to collaborate or work independently – Depending on the project, engineers may need to work in collaboration or independently. They must develop skills in communication, time management, and collaboration.
- Communication – Whether they work independently or as part of a team, they need good communication skills to discuss scheduling and repairs.
Conclusion
Being an electrician is a satisfying and stable career option. Future electricians with a trade school degree in Rhode Island are already leaps and bounds ahead of those who do not have the basics right. Begin your application today to receive a top-rated education from the New England Institute of Technology.
START YOUR ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY CAREER
Earn your degree in Electrical Technology from NEIT and begin your new career path today!
ASSOCIATE'S DEGREE
BACHELOR'S DEGREE
FAQs
How Long Does an Electrician Apprenticeship Take?
Journeyman electricians start as apprentices and complete 2 to 5-years of on-the-job training. During this time, they have to demonstrate the skills required and the ability to work independently. Apprentices usually work under a master electrician.
How Do I Join NECA?
Once you start a business in electrical contracting, erecting, installing, repairing, servicing, and maintaining electrical systems, you can become a National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA) member. NECA members are signatory contractors to hire union electricians.
Is it Safe to Work as an Electrician?
The job does present certain risks from electrical equipment, shocks, and falls, but all electricians work with necessary protective gear. They learn about personal safety and occupational best practices during the training program. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the occupation’s fatality rate is only 1.5%.
It is best to choose the right company, contractor, or union to affiliate with. The employer should have high standards and protocols during training and on-site work.

